|
|
| Chinese
History |
A
Quick Guide to Chinese History |
|
This
is a very quick glance at Chinese history,
and ideal as a pointer to basic facts and 'Who did what
when'.
Chinese history is very complex, and often Kingdoms
are overthrown and disappear, only to reappear centuries
later. This section only mentions the most important
people and events, plus inventions. It covers a period
of some 10, 000 years
For a much more detailed look at Chinese history, please
refer to the era by Dynasty
You are always welcome to contribute - simply drop me
a line
Chinese History Timeline
| Main Dynasty |
Contemporary Kingdoms
or Comments |
| |
|
|
| Ancient China |
|
|
3 Sovereigns and 5 Emperors
|
|
|
| Xia Dynasty 2100–1600 BC |
|
|
| Shang Dynasty 1600–1046 BC |
|
|
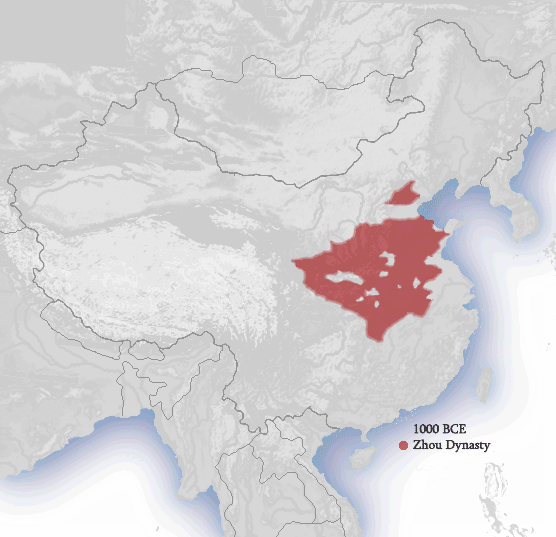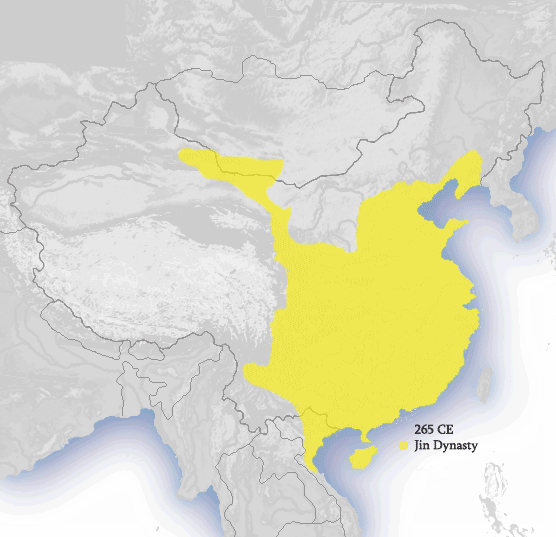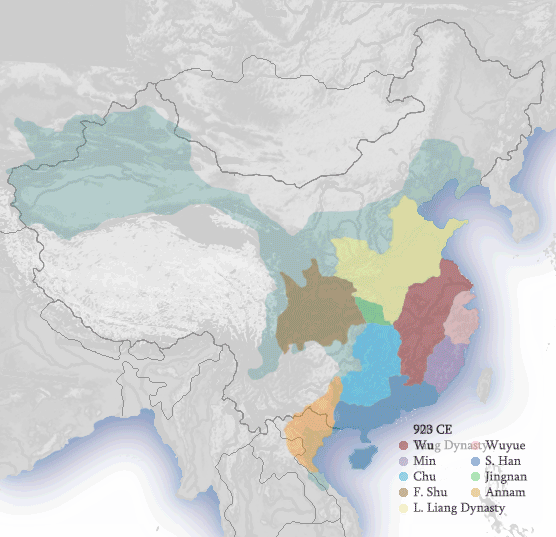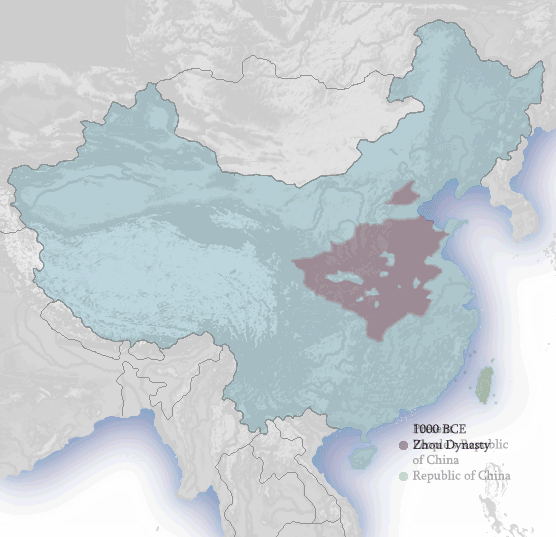
| Zhou Dynasty 1045–256 BC |
|
|
| Western Zhou |
|
|
| Eastern Zhou |
|
|
| Spring and Autumn Period (770
to 476 BC) |
|
|
| Warring States Period (475 to 221
BC) |
Qin Kingdom |
|
| |
|
|
| Imperial China |
|
|
Qin Dynasty 221 BC–206 BC
|
|
|
Han Dynasty 206 BC–220 AD
Western Han
Xin Dynasty
Eastern Han |
|
|
Three Kingdoms 220–280
Wei, Shu & Wu |
|
|
Jin Dynasty 265–420
|
|
|
Western Jin
Eastern Jin |
16 Kingdoms 304–439 |
|
Southern & Northern Dynasties 420–589
|
|
|
| Sui Dynasty 581–618 |
|
|
Tang Dynasty 618–907
( Second Zhou 690–705 ) |
|
|
5 Dynasties & 10 Kingdoms 907–960
|
Liao Dynasty 907–1125 |
| Song Dynasty 960–1279 |
| Northern Song |
|
W. Xia |
| Southern Song |
Jin |
|
Yuan Dynasty 1271–1368
|
|
|
| Ming Dynasty 1368–1644 |
|
|
| Qing Dynasty 1644–1911 |
|
|
| |
|
|
Modern China
|
|
|
| Republic of China 1912–1949 |
|
|
| People's Republic of China (Mainland China)
1949–present |
Republic of China (Taiwan) 1945–present |
| |
Map courtesy of Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_China
|
|
Prehistory
40, 000 BC
The earliest Chinese remains have been discovered near
Shanghai, and date from 40, 000 years ago. These are
Homo Sapiens, and associated with Homo Erectus remains
nearby. There is little in the way of tools, and scientists
conclude that most tools were made of bamboo. Amongst
surviving remnants are jade workings, and extremely
crude clay vessels
20, 000 BC
Excavations near Chengdu and ChongQing in Sichuan Province
reveal human settlements and burial rituals, as well
as sacrificial ornaments, vessels, jewellery, and tools.
10, 000 BC
Early civilisations appear, most notably around the
Yellow and Yangtze River's in modern day Henan and Shaanxi
Provinces. Most mentionable are a tribe called the Xing
Long Wa Circa 8, 000 BC
3 Sovereigns
Records from this period are usually treated as Myths
and Legends, but new data is showing that accounts reflect
real history and real people
Creation
The 3 Sovereigns are: The Heavenly Sovereign Fuxi, The
Earthly Sovereign Nüwa (Adam and Eve?), and their
son, The Human Sovereign Shennong. Shennong is credited
with inventing farming, the plough and fishing, medicine;
and also money and places to exchange goods. This could
be said to represent the dawn of civilisation
5 Emperors
The 5 Emperors are: Huangdi - The Yellow Emperor, Zhuanxu,
Emperor Ku, Emperor Yao and Emperor Shun. All these
"emperors" were only people with great contributions
or famous rulers of tribal unions. From the Bamboo Annals
and Classic of History, their positions are known to
have been attained by election by other chiefs in the
tribal unions. When they die, their children may succeed
the positions of the ruler of their own tribe, but not
the position of the ruler of the tribal union
The most notable is The Yellow Emperor, and simply put
-circa 5, 000 BC Huang Di defeated Yandi and Chi You
in the river valleys of Henan province, and became the
first leader of a united Chinese people. Han Chinese
trace their direct ancestry back to Huang Di
The 3 Emperors
To avoid confusion: Yao and Shun are also known as the
Three Emperors, and, along with Yu the Great, founder
of the Xia dynasty; and were considered to be model
rulers and moral exemplars by Confucians in later Chinese
history
Early Kingdoms
1. Huang
Di, The Yellow Emperor - created the first
Chinese Nation
2. Da Yu, Yu the Great - was the person who reunited
fledgling China after The Great Flood, and created the
Xia Dynasty
Days Before Empire
Xia Dynasty
- Circa 2, 000 BC
Highly advanced Bronze smelting and weaponry, war chariots,
first pottery and writing
Shang Dynasty
- Circa 1600 to 1046
Regarded as the first proper Chinese Dynasty
Writings indicate common usage of thinking such as:
politics, economy, culture, religion, geography, astronomy,
calendar, art, and medicine. Tomb excavations reveal
that women were sometimes great military leaders.
China was basically a 'Closed Country' during the Shang
dominion
Zhou Dynasty
- Circa 1054 to 256 BC
The longest lasting of all Chinese Empires, which gave
rise to modern Chinese culture, literature, and arts.
Modern Chinese writing is traced back to the Zhou period
specifically. The Zhou also cemented the earlier beliefs
that the Emperor was of divine birth, and spoke directly
to the heavens
The Zhou continued to use Bronze, whilst Iron smelting
techniques were quite advanced in Southern China, and
outside of their sphere of influence and control. Fragmentation
eventually led to the Zhou being overthrown, but they
reappear later in Chinese history
Days of Empire
Qin Empire
(221 to 206 BC)
Huang Di, aka Qin Shi Huang (And also verbalised as
The Yellow Emperor - except the Chinese characters are
different but sound the same), overthrew the Zhou, and
united China, becoming the first Emperor of all China
Foreigners from all over the world would naturally pronounce
‘Qin’ as ‘Chin’. The intimate
form of this word is to add ‘ah’, therefore
they became widely known as the 'Qin-ah' or ‘Chin-ah’
people = China.
This Empire lasted for a few years only, but was decisive
in the formation of what we now refer to as Modern China.
Therefore, Qin Shi Huang is given the title of Founder
of China. However the Qin began under King Zhaoxiang
in 306 BC, and they actually annihilated the Zhou Kingdom
in 255 BC
Qin Shi Huang built the first Great Walls of China,
and also developed the existing canal and irrigation
networks substantially. It is thought his engineers
developed 'Sea Level' as a base measurement for projects,
and a concept that does not reappear in China for another
1, 200 years
Qin Shi Huang died of madness due to Mercury poisoning,
which he ingested daily as a medicine His mausoleum
(Like a Long Barrow) has been uncovered, and it supports
tales that his lands were so rich = that they flowed
with liquid silver
Han Dynasty
(202 BC – 220 AD)
The vast majority of modern Chinese peoples are ‘Han’
and come from, or were assimilated into this group.
The Han brought Confucianism to China, and extended
dominion and trade Westwards as far as the Caspian Sea.
They had documented trading relations with the early
Roman Empire, such as in 166 BC. This was overland,
and later became known as ‘The Silk Road’
Perhaps most notably for European history, they fought
and repelled the ‘xiongnu’, who are regarded
as being the forefathers of The Huns
The Han ruled an area that can modestly be stated as
being the Eastern part of modern China, including Northern
Vietnam, but excluding Tibet. However, religion dictates
that modern Buddhism came from Tibet around this time,
as evidenced by the Chinese fable ‘Journey To
The West’, which you will know simply as ‘Monkey’
Post
Han
As in Europe, and especially in UK, this was a time
of wars, with many factions claiming power and kingdoms,
only to be replaced by other pretenders to the throne.
Have a look at our section 'Post
Han' if you want to know more
During this period China descended into various factions
and warring states (Again)
Sui Empire (581–618)
A short-lived and overly maligned Dynasty, mainly because
of their overzealous use of force. However, they achieved
one great thing, and that was to reunite China. They
built The Grand Canal and extended The Great Wall +
reformed land use. Without them it is likely that China
would nowadays be many separate Countries!
Tang Empire
(618 – 907)
The Tang dynasty gave rise to many arts and crafts that
still flourish today in China. They also accepted both
Buddhist and Taoist beliefs, and implemented an advanced
system of feudal land use known as ‘Equal Field
System’. They also kept trade routes open, especially
to the West (Overland), and South by sea (Guangzhou).
Empress Wu Zetian, the only female ruler of China to
do so in her own undisputed right.
Also worthy of mention: Princess Wencheng in the early
Tang Dynasty - a wonderful woman diplomat.
Empress Zhangsun of Tang Dynasty, and wife of Emperor
Taizong - a good model both as wife and empress
Interestingly: Culture flourishes and women also have
equal rights
Post-Tang
(907 - 1115)
The Tang dynasty is overthrown and followed by another
unruly period.
Pertinent factors for foreigners to China: The Dali
Empire based from Yunnan province comes and goes, but
brings conflict and understandings between nomadic Tibetan's
and lowland Chinese. You may want to trace your modern
thinking about Tibet back to this era
Song
Empire (1115 – 1254)
Another time of turmoil and great advances in science
and arts. China had it’s Capital in Hangzhou
Gunpowder is used in warfare for the first time, meaning:
Guns, cannons, and mortars are invented; and used!
The Last 900 Years - Pay Attention!
If you haven't already got the hang of Chinese history
by now, in that the same pretenders to the throne keep
reappearing in new guises at later dates - then wake-up!
This next period is really all about interactions for
ultimate control between: The Mongols, The Jin (Jurchen
aka Qing), and existing Chinese Royal Houses.
Traditional Chinese history does not include: West China,
Tibet, The Dali Empire of Yunnan - at least up until
the Mongol invasion. Southeast China is more of an autonomous
trading partner rather than a vassal state. Therefore,
you should consider these years in context, and know
it is really all about control of the Yellow and Yangtze
River valley's by Kingdoms that have been warring for
millennia
Now, let us continue...
Yuan Empire
(1271 – 1368)
This represents the Mongol invasion(s) of China, which
went as far as the shores of Japan, included the domination
and subjugation of Tibet, most of eastern Russia, and
a lot of Europe.
The names you may know from history books are Genghis
Khan, and his grandson Kublai Khan –> in xianadu
did kublai khan a pleasure dome erect, etc… and
it's ruins lie just outside modern Beijing!
What you may not know is that the Mongols were divided,
as some like Kublai Khan wanted to adopt Chinese culture,
whilst others did not.
My personal understanding is that the Mongol tribes
brought an understanding of international money to China,
as witnessed by the precedent that the names for the
Yuan Empire, and Chinese currency are still synonymous
to the present day = Yuan
Ming Empire
(1368 – 1644)
After the demise of the Mongols, the Ming Dynasty reinvented
China; bringing with them culture, arts and excellence
of skills and thinking. Your treasured china may be
named after this Dynasty?
Zheng He assembles a fleet and sails the known world.
Trading relationships are established with East African
States and Chinese control reaches as far as Turkestan..
China is 'Open' during the beginning of this Dynasty,
but later it becomes more paranoid and 'Closed'. The
Ming created a bureaucracy that at first provided
good governance to all the people, but later led directly
to the demise of the Dynasty = Too much red tape!
|
Qing
Empire (1644 – 1911)
|
|
The Qing are not Chinese, but come from Manchuria in
what is now Southeast Russia, although it had been under
Chinese rule for centuries. They are known for centuries
as 'The Jin', a Chinese reference for The Jurchen People.
The Qing do not have to storm the Great Wall, the gates
are opened and their small army is let through - such
was the discontent with current central government manipulations
in ordinary people's everyday lives. Europe should learn
from this lesson, or ignore it at their peril. I digress...
The Qing simply took over power without a struggle,
and assimilated themselves as Chinese rulers. This charade
lasted for centuries, although the first warning signs
of peasant revolt appeared as early as 1800. China became
an ever more 'Closed' and insular culture as their reign
progressed, but Chinese culture of the Qing variety
flourished
The Qing would probably not have been overthrown, was
it not for the greed of Western Powers: England, France,
Germany, Russia, and Japan (And also: USA, Spain, Portugal,
and the Dutch [Netherlands]). |
Anyway...
You may have heard about things such as:
• The Opium Wars
• The Boxer Uprising
• The Xinhai Revolution and contemporary Wuchang
Uprising
• Or wondered why China was fighting alongside
Britain inside Burma during the late 17th Century
The latter Qing Empire is a very complicated period
of world history. You can read our interpretation of
the main events here: Qing
Empire
Modern China
(1912 to Present)
Well ... this is a whole lot more complex than anything
above!
Simply:
This is a time of turmoil, and events follow this generalised
pattern: End of Empire, Dictatorship, Democracy, Dictatorship,
Civil War, Japanese Invasion, Democracy, Civil War [re-Continued
after a break of 8 years], Communist State, Ideological
Communist State, New Way for Communism + Democracy
You need to know about five people and world events:
1. Dr Sun Yat Sen - patronaged the
first Republic of China. His Party was called the KuoMingTang
(KMT)
2. Mao ZeDong - Founded the Peoples
Republic of China in 1949. First Chairman and foremost
modern forefather
3. Deng XiaoPing - The creator of Modern
China as we know it today and 'The Policy of 'Openness'
4. Jiang Zemin - Developed the Openness
Policy and created the 'Three Represents' principles
5. Hu Jintao - Created the 'Scientific
Development Concept'
To date, six men have held the office of the president
of the People's Republic of China: Mao Zedong, Liu Shaoqi,
Li Xiannian, Yang Shangkun, Jiang Zemin, and the current
president, Hu Jintao
China today has 9 political parties, not just one!
Also note the Second World War started in China in 1937
with the Japanese invasion ... your local history lessons
may have missed this fact? During these times, China
was enduring a Civil War; which was 'Put on hold' in
order to defeat the Japanese invaders.
Most notable events include 'The Long March', instigated
by Mao to escape Nationalist forces let by Chiang Kai
Shek. It lasted over one year and has similar standing
to the Allies withdrawal from Dunkirk. From this new
base, Mao (Assisted by Zhou Enlai) engineered social
and peasant reforms, taking popular support in the countryside.
They also created modern guerrilla warfare, and eventually
won! The KMT fled to Taiwan, taking with them much treasure
and 2 million people.
Chinese peoples are like a very large family. Like any
family, they do not always agree wholeheartedly with
each other. You should regard China and Taiwan as both
believing in a united China - and one day quite soon
this may become a reality. The framework is already
in place, with the democracies of Hong Kong and Macao.
China is proud to boast: 'One Country, two systems'
The country of modern China is just 30 years old, and
follows the way forwards expounded by Deng XiaoPing.
This has developed over several decades, and now finds
a modern China ready to take its true place on the world
stage. It is led by a young and proactive government
under the leadership of President Hu Jin Tao and Premier
Wen Jia Bao
To learn more about Chinese government, please click
the link below for the excellent Chinese Government
website in English language - which is full of current
news, reviews, and details of China's political structure
and hierarchy
http://english.gov.cn/index.htm
Please see our History
of Modern China for full details of the
events of this century in a nutshell
Here is China!
|
|
This information is as supplied by Wikipedia, as dated
March 2009 or later, and/or other reliable sources.
Maps (Unless stated otherwise)
are provided in association with Thomas Lessman
Web: www.worldhistorymaps.info
Disclaimer:
Please check this information yourself as it may alter
without notice, and whilst we try our best to ensure
it is correct, please do not hold us responsible for
any errors - this is intended as a simple guide only |
|
| Search
this Website |
|
|
| Our
Friends |
Excellent
& Free Online Chinese Language Portal
Thousands of free print-friendly Chinese reference sheets,
tests and revision aids.
Easy Learning format &
Listen to Spoken Words |

Professional
Visa Services
Company
Formation Packages
.
|

British Foreign Office
Resource and Advice for Travellers Worldwide |

Chinese Embassy in UK
Information About China
International Relations
Visa & Consular |
UK Embassy in China
Information About UK
International Relations
Visa & Consular |

|
Excel
Education |
Languages Courses
Study Abroad
Employability
Summer Camps
Information for Teachers |
|

Excellent and relaxing base to
explore this most beautiful of regions in all China! |
Down The Road.org
How We Traded Our Ordinary Lives For a Global Bicycle Touring Adventure

See
Us in China |

Empowering Underprivileged Children
& Their Communities = Worldwide |
 |

Based in Shangri-la,
Yunnan
Province
Dedicated to Exploring Remote Areas of China
Committed to Nature Conservation and Preserving Ethnic
Cultures & Traditions
|

Based in Xi'an,
China's Premiere Travel Agency and International Travel
Community -
Committed to providing:
Best travel deals & current information for all
International Travellers |

Pearl Dragon
Vast
Online Trading and Information Resource
Link goes to Chinese Tourism and Galleries Section |
|